In this short session you will be introduced to:
- Distinction between structured and unstructured data
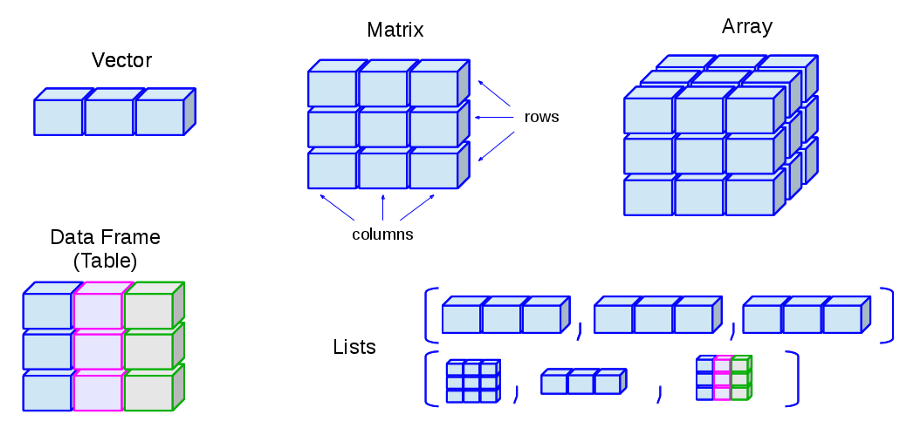
- Crashcourse in data dimensionality.
- The concept of “tidy” data.
Updated August 29, 2022
In this short session you will be introduced to:
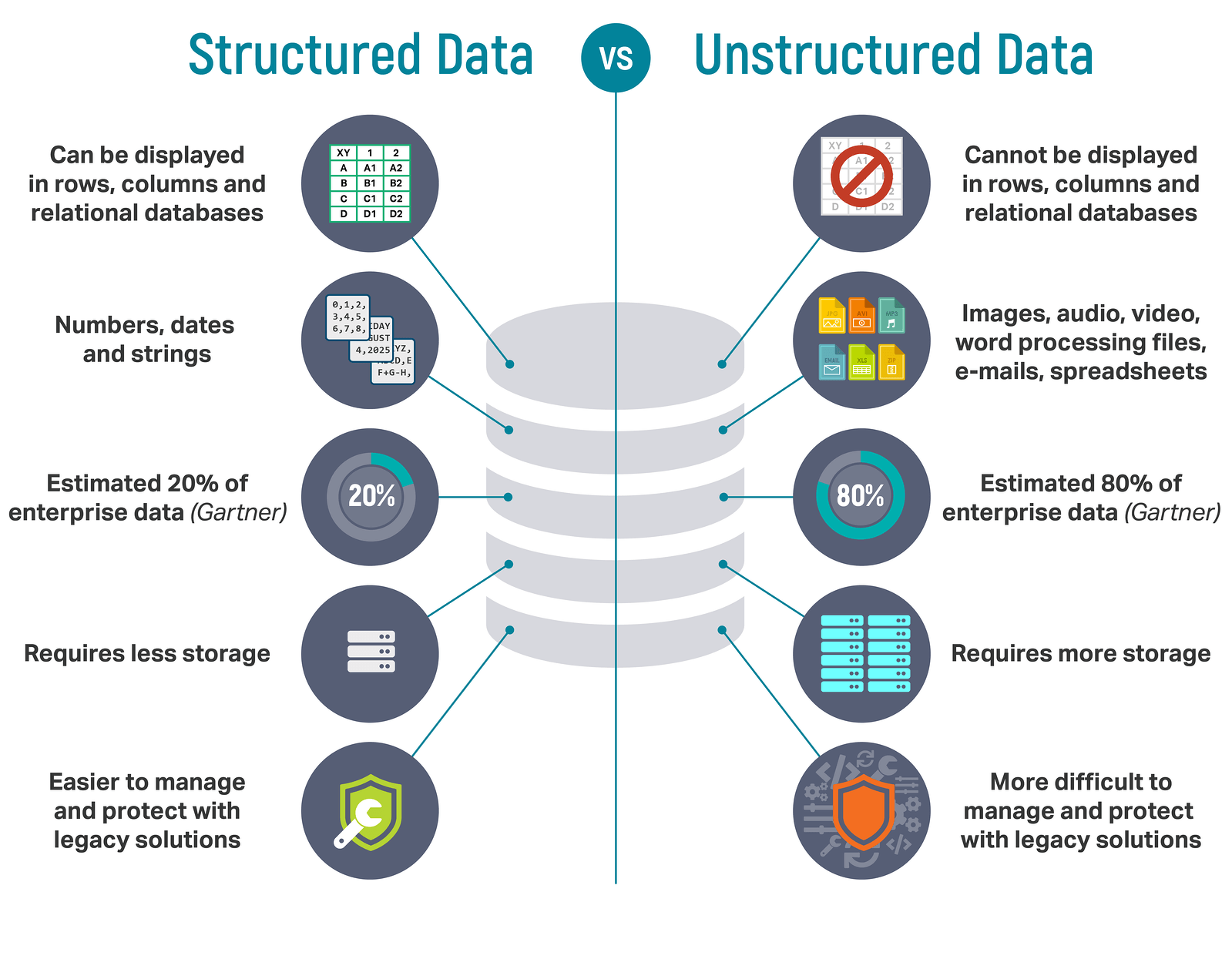
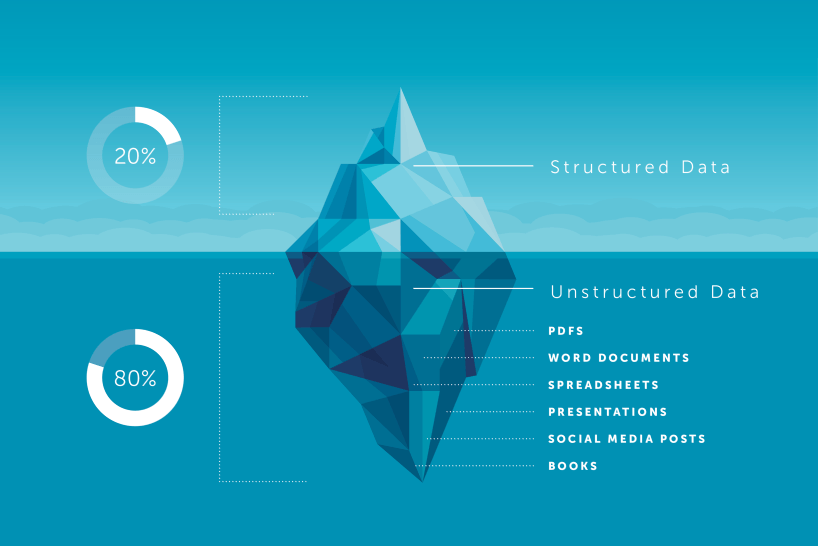
= Data that can be meaningful expressed in a tabular (row/column) format.
= everything else.
One big part in the preprocessing of ML/DS projects is often to bring unstructured data in a structured format.
You might need to handle some unstructured data, yet for the most part this is not content of this but later modules.

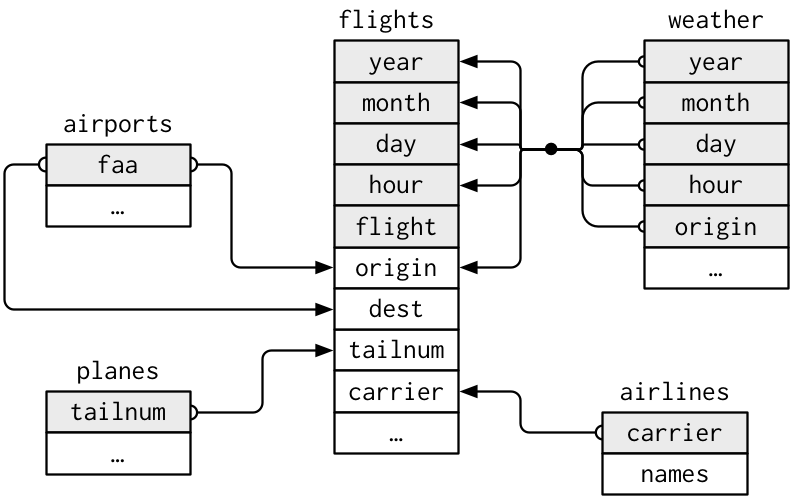
Why ensure that your data is tidy? There are two main advantages:
1.Consistent way of storing data. If you have a consistent data structure, it’s easier to learn the tools that work with it because they have an underlying uniformity. 2. Likewise, consistency in format eases the reuse of existing workflows to new DS/ML projects. 3. When working with structured data, having a row for every unit of observation facilitates analytic .